Download *.tar.gz unix-compressed file (zipped in addition)
Summary:
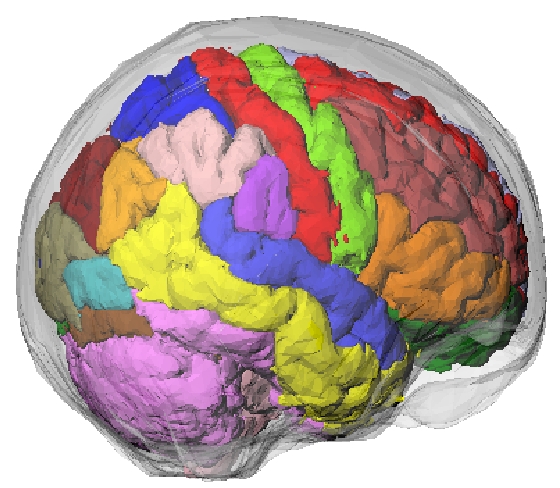
- Based on a segmented MRI dataset of a normal subject, including ~100 structures (listed below).
- The program also allows simulation of motion (rigid; 3 translations, 3 rotations).
Reference:
Please consult (and reference) the following work wherein the construction of the phantom has been described:
A. Rahmim et al., Accurate event-driven motion compensation in high-resolution PET incorporating scattered and random events , IEEE Trans. Med. Imag., vol. 27, pp. 1018-1033, 2008.
Technical description:
Voxelized phantoms are problematic in that they are fixed to a particular spatial resolution, and also result in interpolation errors when modeling motion (e.g. the volume of a voxelized object may not be conserved after rotation). Alternatively, a mathematical brain phantom was developed, containing continuous structures and thus avoiding the need for interpolations when introducing motion. The brain phantom was constructed using subdivision surfaces. Subdivision surfaces can be used to efficiently model structures with an arbitrary topological type, such as the brain, skull, muscle tissue, and vasculature. Surfaces were modeled based on a segmented MRI dataset of a normal subject. The dataset consisted of 181 slices of the brain (pixel-sizes/slice-widths of 1.0 mm’s). Nearly 100 structures in the brain were identified. A software application was written using the Visualization Toolkit (VTK) to create 3D polygon surfaces. The VTK marching cubes algorithm was first used to create an initial polygon model for each structure. The polygon model was then optimized using the mesh optimization and smoothing routines of the VTK software.
Brain Structures:
The following ~100 structures are included in the phantom, which can be easily merged by assigning similar values.
- Grey “superior frontal gyrus” right
- “superior frontal gyrus” left
- “middle frontal gyrus” right
- “middle frontal gyrus” left
- “inferior frontal gyrus” right
- “inferior frontal gyrus” left
- “precentral gyrus” right
- “precentral gyrus” left
- “lateral front-orbital gyrus” right
- “lateral front-orbital gyrus” left
- “medial front-orbital gyrus” right
- “medial front-orbital gyrus” left
- “cingulate region” right
- “cingulate region” left
- “medial frontal gyrus” right
- “medial frontal gyrus” left
- “superior parietal lobule” right
- “superior parietal lobule” left
- “supramarginal gyrus” right
- “supramarginal gyrus” left
- “angular gyrus” right
- “angular gyrus” left
- “precuneus” right
- “precuneus” left
- “postcentral gyrus” right
- “postcentral gyrus” left
- “superior temporal gyrus” right
- “superior temporal gyrus” left
- “middle temporal gyrus” right
- “middle temporal gyrus” left
- “inferior temporal gyrus” right
- “inferior temporal gyrus” left
- “uncus” right
- “uncus” left
- “medial occipitotemporal gyrus” right
- “medial occipitotemporal gyrus” left
- “lateral occipitotemporal gyrus” right
- “lateral occipitotemporal gyrus” left
- “amygdala” right
- “amygdala” left
- “parahippocampal gyrus” right
- “parahippocampal gyrus” left
- “occipital pole” right
- “occipital pole” left
- “superior occipital gyrus” right
- “superior occipital gyrus” left
- “middle occipital gyrus” right
- “middle occipital gyrus” left
- “inferior occipital gyrus” right
- “inferior occipital gyrus” left
- “cuneus” right
- “cuneus” left
- “lingual gyrus” right
- “lingual gyrus” left
- “insula” right
- “insula” left
- Caudate “caudate nucleus” right
- “caudate nucleus” left
- Putamen “putamen” right
- “putamen” left
- “globus palladus” right
- “globus palladus” left
- “thalamus” right
- “thalamus” left
- White “corpus callosum”
- “subarachnoid cerebro-spinal fluid”
- “third ventricle”
- “fourth ventricle”
- “lateral ventricle” right
- “lateral ventricle” left
- BrainStem “brain stem”
- “white matter”
- “frontal lobe WM” right
- “frontal lobe WM” left
- “occipital lobe WM” right
- “occipital lobe WM” left
- “parietal lobe WM” right
- “parietal lobe WM” left
- “temporal lobe WM” right
- “temporal lobe WM” left
- “background”
- “scalp”
- “skull”
- “dura and sinuses”
- “hippocampal formation” right
- “hippocampal formation” left
- “nucleus accumbens” right
- “nucleus accumbens” left
- “fornix” right
- “fornix” left
- “posterior limb of internal capsule inc. cerebral peduncle” right
- “posterior limb of internal capsule inc. cerebral peduncle” left
- “subthalamic nucleus” right
- “subthalamic nucleus” left
- “anterior limb of internal capsule” right
- “anterior limb of internal capsule” left
- Cerebellum “cerebellum” right
- “cerebellum” left